Introduction to Automation and Process Control
Definition of Automation
Replacement of the human operator by an artificial operator, in the execution of a previously programmed physical or mental task. One has to control the system in order to automate it.
Types of control schemes
There are basically two types of control: Open Loop and Closed Loop
The open loop has the following structure. It receives a command or reference signal. The controller calulates an input signal for the actuator. The output of the actuator starts manipulating the system. Since the controler does not receives any feedback on how the systems reacts on the command the results might be different from the desired behaviour. Examples for the application of open loop control are: A tennis player who hits the ball, if you turn on a light in you room or a DC motor without sensors.

To improve the resulting behaviour and be able to correct possible differences between the commad value and the resulting value, one can implement sensors that observe the resulting behaviour of the systems or process. This sensors return the current behaviour to the controller and the controller can correct the input signal to the actuator. The following figure shows the general structure of a close loop control.
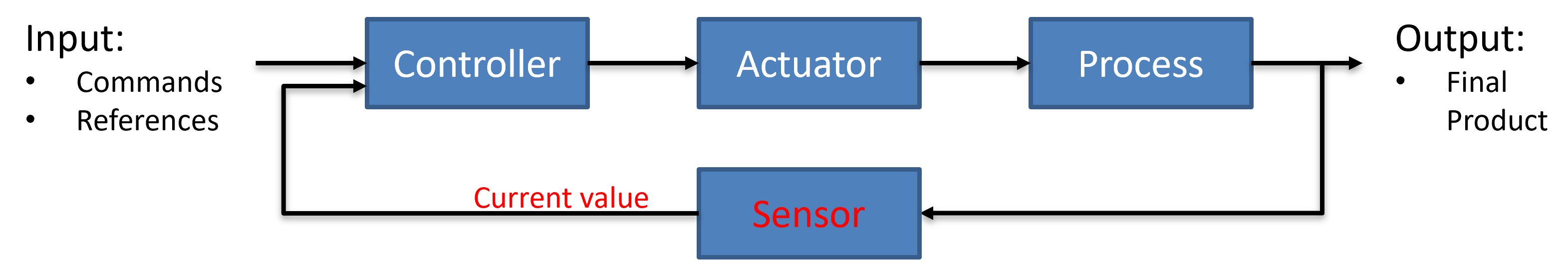
Industrial Process
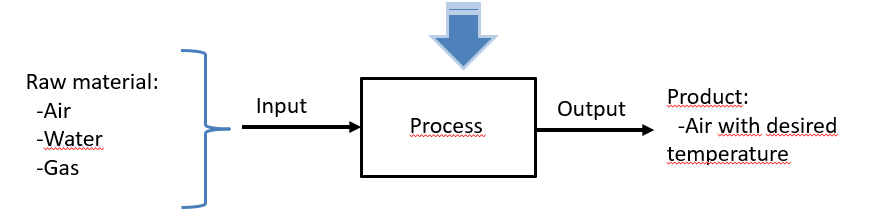
An industrial Process is a set of actions for transporting and transforming raw materials to obtain a final product.
Types of Industrial Processes
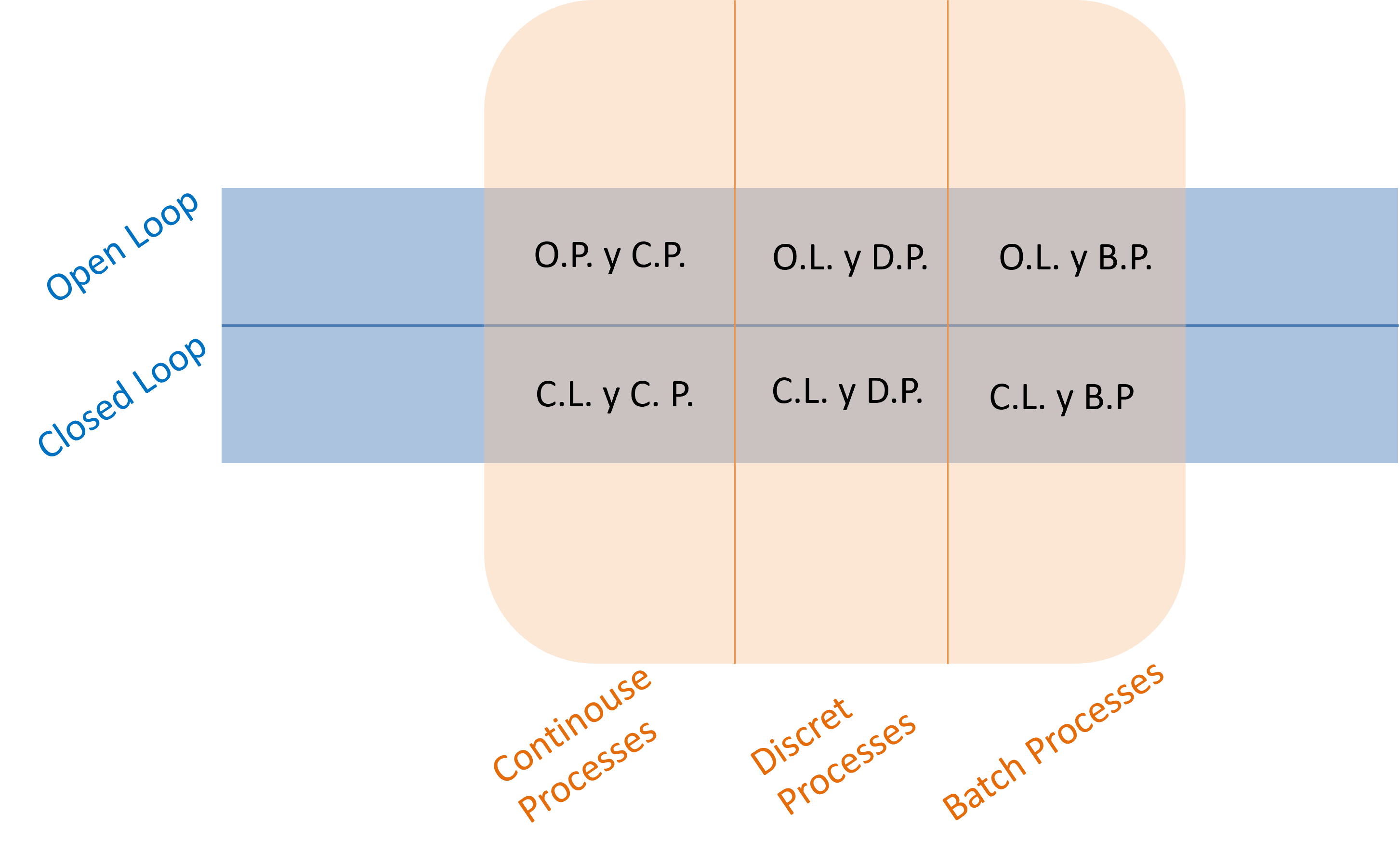
There are different types of proceses within industrial processes: Continuous Processes, Discrete and Processes Non-continouse Processes by batches. Each type will be explained shortly.
Continuous Processes:
Uninterrupted process over time in which analog variables (temperature, speed, etc.) are manipulated.
Process in which raw materials are constantly entering at one end of the system, while at the other end a finished product is continuously obtained.
Example: Heating System Someone defines the requiered temperature in the room. The input value can be done by different types of devices, digital or analogue inputs, for example. At the same time, the current room temperature is measured and compared to the reference. The difference between these two values are the input to the controller and the controller calculates the new opening value for a valve that opens the gas flow to the burner. The room gets warmer (or not) and a new temparature is measured. This new temparature value is then compared again to the reference value.
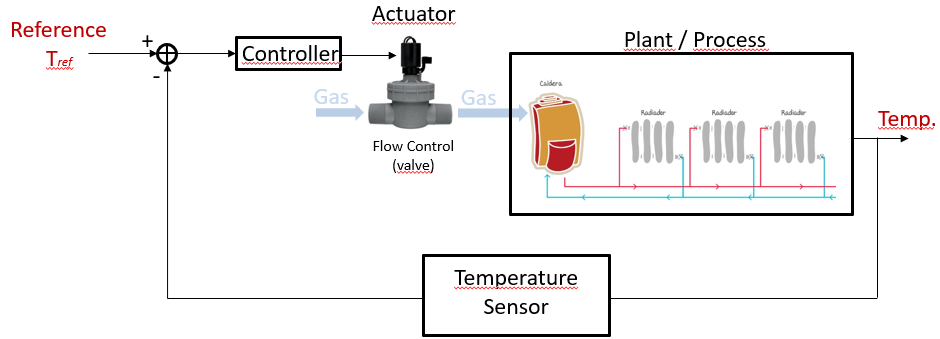
Discrete Processes
Processes that involve variables that can take a finite number of possible values or states.
Processes in which the output product is obtained through a series of operations.
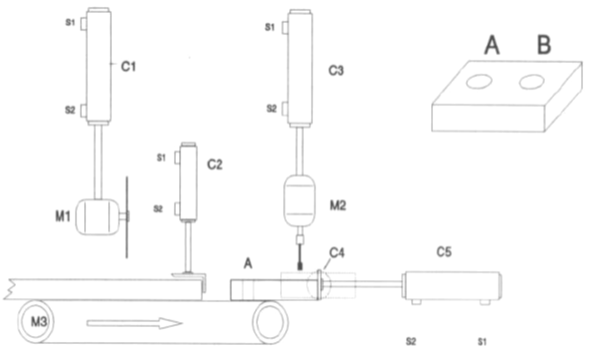
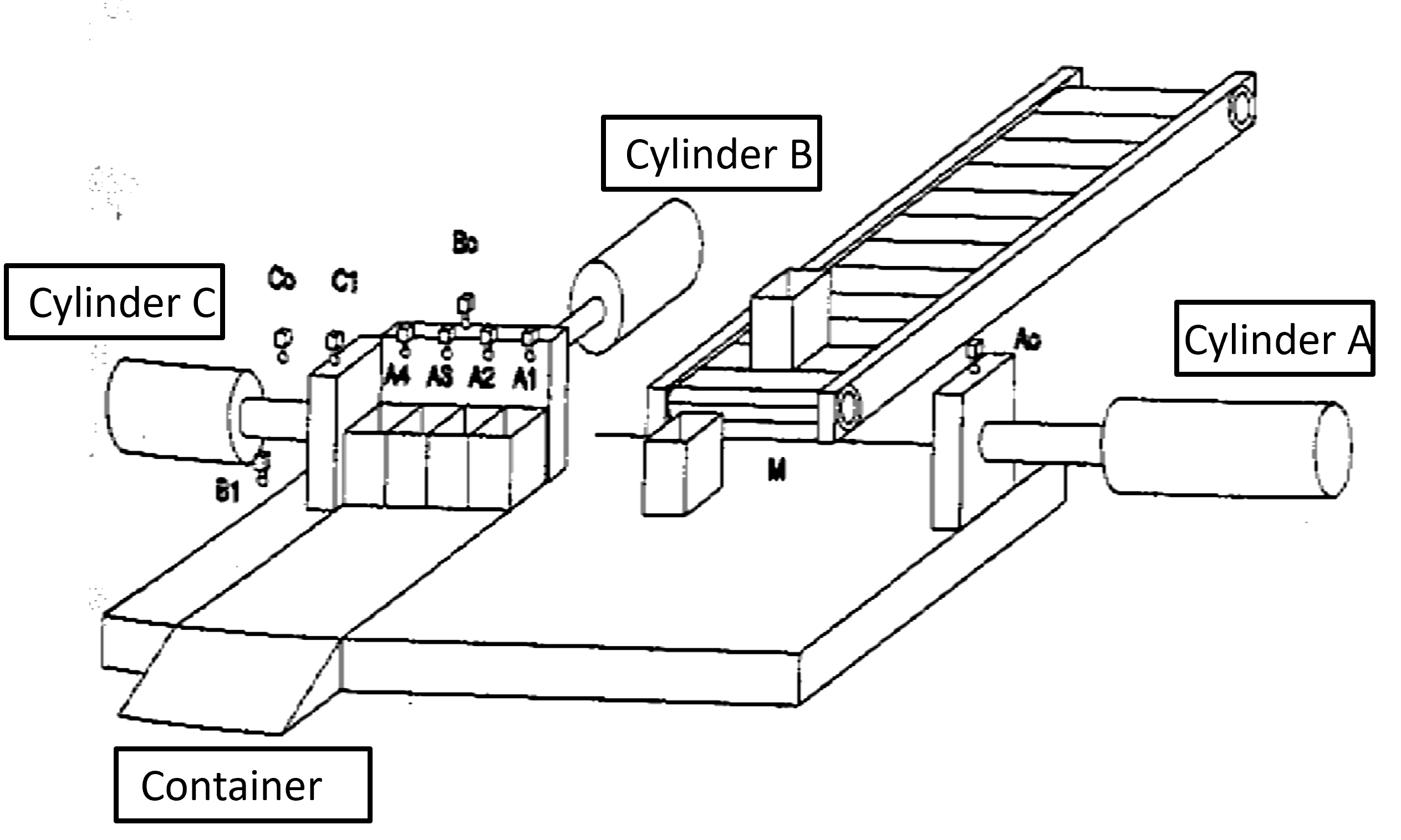
Example: Production of metalic pieces
Steps:
Cut the piece
Transport the piece
Drilling A
Drilling B
Take the piece out
Non-continuous Processes by batches
Processes where the final product is made up of different components.
Steps:
Position pieces C, D and E
Position piece B
Position piece A
Return cylinders pieces C, D and E
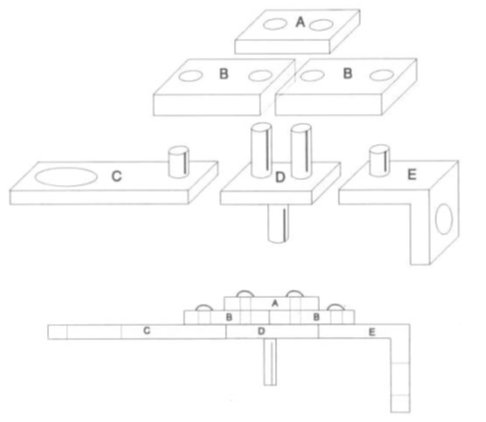
Box Stacker:
Resume: Types of processes and types of control
Industrial Automation
Total (or partial) elimination of human intervention in manufacturing processes, carrying out calculation and decision functions.
Typical examples with pneumatic application can be found in the food and drug industry (example) or in the textil industry (example).